Revolutionizing Drug Delivery: Advances in Oral Thin Film Technology
The Intersection of Drug Delivery and Speed
Imagine medication that dissolves on the tongue within seconds and arrives at a patient’s doorstep by the next day. This is the promise of fast-dissolving oral thin films (OTFs) combined with advanced rapid delivery services. OTFs are ultra-thin polymer strips loaded with active drugs. Placed on the tongue or inside the cheek, they instantly wet with saliva and release medication without chewing or water pharmaceutical-business-review.com
drug-dev.com. This makes them highly patient-friendly. For example, an estimated 15 million Americans have difficulty swallowing pills, and roughly half of adults over 60 will experience dysphagia in their lifetime contractpharma.com. OTFs – often flavored and perforated for precise dosing – address this need directly drug-dev.com.
At the same time, modern pharmaceutical logistics are breaking speed barriers. Nationwide courier networks and postal services can now deliver life-saving treatments almost instantly. In the COVID-19 pandemic, for instance, the U.S. Postal Service (USPS) delivered over 900 million at-home COVID-19 test kits – with an average of just 1.2 days from shipment to deliveryabout.usps.com. This USPS COVID test delivery program showed how rapid delivery channels can distribute critical healthcare resources at scale. Together, fast-acting OTF medications and lightning-quick delivery networks are reshaping healthcare by making drug therapy more convenient and more accessible than ever.
Understanding Oral Thin Films (OTFs): Science and Benefits
What Are OTFs?
OTFs are tiny sheets (often the size of a postage stamp) made of water-soluble polymers and plasticizers, into which the active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) is dispersed drug-dev.com . They come in two main flavors: orodispersible films that dissolve immediately in saliva, and mucoadhesive films that stick to the oral mucosa (under the tongue or inside the cheek). In either case, the film rapidly hydrates and disintegrates, releasing the drug. A portion of the drug can be absorbed directly through the oral mucosa into the bloodstream (bypassing the gut), while the rest is swallowed and absorbed in the stomach or intestines .
How OTFs Work: Hydration & Rapid Absorption
When an OTF is placed in the mouth, saliva is all that is needed to activate it. Unlike tablets or capsules, no chewing or water is requireddrug-dev.com. The large surface area of the film promotes ultra-fast wetting and dissolution. Once dissolved, the medication becomes instantly bioavailable. Because some drug can enter the circulation via the oral mucosa, OTFs can avoid first-pass metabolism and achieve faster onset of action pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.govpmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. In emergency situations (like allergic attacks or pain crises), this rapid effect is especially valuable.

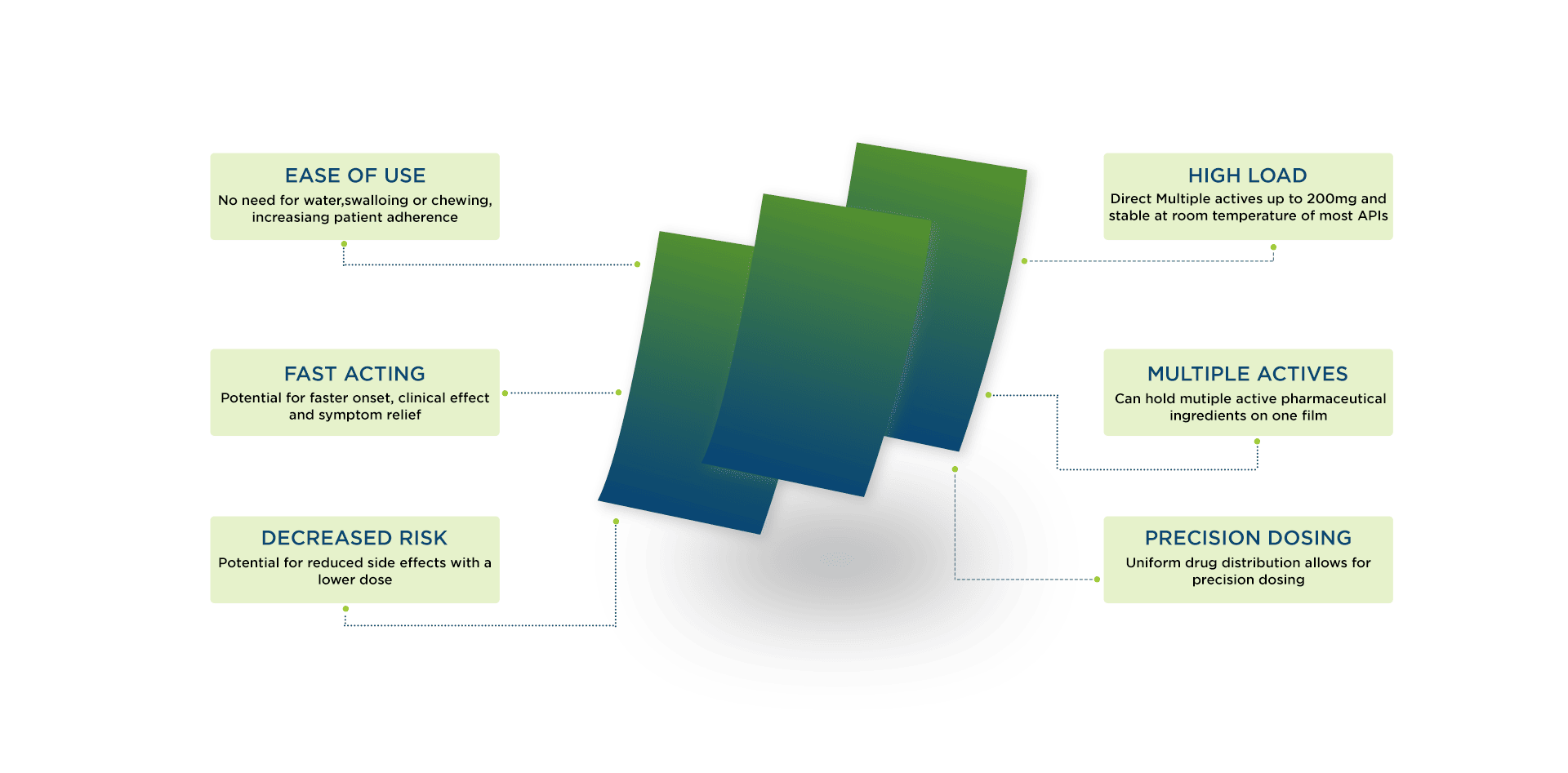
Advantages of OTFs
Oral thin films offer numerous practical advantages over traditional dosage forms:
-
No water needed: Patients can take OTFs anywhere, anytime, without water. This eliminates choking risks and makes dosing convenient during travel or in resource-limited setting.
-
Safe for special populations: OTFs solve swallowing challenges. Studies note that pediatric and geriatric patients – who make up large patient groups – benefit greatly since they often have trouble with pills. Pleasant flavorings and perforations for dose flexibility make the films more acceptable for children and the infirm.
-
Higher bioavailability: By partially bypassing the gastrointestinal tract, OTFs can improve bioavailability. In fact, they “provide enhanced bioavailability for less water-soluble drugs” by dissolving rapidly in the mouth. This means lower doses can achieve therapeutic effect, often with fewer side effects.
-
Rapid onset: Since OTFs dissolve in seconds, their effects appear much faster than equivalent tablets. They are ideal for situations requiring immediate relief (for example, acute nausea or migraine). In one review, OTFs were highlighted as important “in cases of emergency and when an immediate-onset effect is desired”.
-
Ease of use: Films are stable, portable, and do not leave residue. They can be precisely dosed (no measuring like with liquids) and do not interfere with speech or eating. These practical benefits improve patient compliance.
Applications of OTFs
Fast-dissolving films are being explored across many therapeutic areas. Examples include:
-
Insomnia: OTFs can deliver sleep aids like melatonin quickly (a Circadin melatonin strip is under development), allowing patients to take a dose easily at bedtime.
-
Chronic diseases: Small-molecule drugs for hypertension, diabetes, or neurological diseases are being reformulated as thin films for patient convenience. For instance, ADHD medications and migraine therapies are now available as oral films.
-
Vaccines & biologics (future): Research is ongoing into OTFs for vaccines or large molecules, leveraging rapid absorption and eliminating needles.
-
Mental health: Films offer discreet dosing for medications used in schizophrenia or depression.
-
Anti-nausea & anti-pain: An ondansetron (antiemetic) film is one example, allowing cancer patients to swallow medication without water during chemotherapy. Likewise, buprenorphine/naloxone films (for opioid addiction treatment) have been FDA-approved.
-
Neurological & rare diseases: Thin films have delivered therapies for Alzheimer’s, ALS, Parkinson’s and more. In short, any condition benefiting from fast or discreet oral dosing is a target for OTF formulations.
The market is growing quickly. A recent analysis projects the global OTF market rising from about $1.2 billion in 2015 to ~$2.1 billion by 2025contractpharma.com. Around a dozen oral film products have already earned FDA approval, with many more in the pipelinecontractpharma.com. This momentum reflects broad demand for innovative, patient-friendly drug delivery systems.
The Role of Rapid Delivery Services in Healthcare
Why Speed Matters
In healthcare, time can be critical. Medications like insulin, epinephrine, or anti-infectives often cannot wait. Every hour saved in delivery can mean better outcomes. The COVID-19 pandemic underscored this: to facilitate home testing, postal and courier networks were pressed into service on an unprecedented scale. As mentioned, USPS alone has distributed hundreds of millions of test kits, maintaining an average of only ~1.2 days from dispatch to arrival. This level of service illustrates how a capable logistics backbone can underpin public health initiatives. In the same way, rapid couriers ensure that a patient’s prescription – whether a life-saving drug or an urgent supplement – reaches its destination quickly and reliably.
Key Players in Rapid Healthcare Delivery
Several logistics providers specialize in urgent, on-demand delivery for medical needs:
-
Dynamex Rapid Delivery: A leading same-day medical courier in the U.S. and Canada, Dynamex operates a network of hubs and drivers focused on door-to-door rush deliveriesannualreports.com. It handles on-demand requests and also integrates air carriers when longer distances are involved, ensuring time-critical shipments arrive that day
-
Rapid Courier LLC and Other Med‑Only Couriers: Many regional and local courier services now focus exclusively on healthcare. For example, companies branded as Rapid Courier offer 24/7 same-day specimen and medication delivery within metro areas. These same-day medical couriers often provide dedicated, secure transport for pharmacy-to-patient routes.
-
Amazon Pharmacy / “Amazon Rapid Express”: Tech-driven giants are entering the field. Amazon Pharmacy has launched same-day prescription delivery in major cities, leveraging its massive logistics infrastructure Plans are underway to expand to dozens of cities. In fact, Amazon is even experimenting with drone delivery – one Texas location reported medication deliveries in under an hour via drone. By integrating pharmacy dispensing with their “Prime” network, Amazon effectively offers a rapid-delivery healthcare service.
-
Others (UPS, FedEx, DHL, etc.): Large carriers have specialized divisions (like FedEx Custom Critical) for medical logistics. These firms offer expedited, temperature-controlled shipping for bulk medical supplies and organs alike. While not purely same-day, they provide next-day or overnight global reach.
-
Postal Services: Traditional postal systems (like USPS) also play a role. Their unparalleled reach (“nearly 167 million addresses covered”) makes them ideal for programs like mail-order pharmacies or government health outreach. In recent years USPS and other mail carriers have partnered with healthcare agencies to ensure nationwide delivery of vital medical items (vaccines, test kits, etc.).
Tech Enablers: Tracking, Cold Chain, AI
Modern technology underpins these rapid networks. Real-time tracking is now standard: shipments are equipped with GPS and IoT sensors so every package is visible online. This is critical for temperature-sensitive drugs. As one industry review notes, “AI can improve logistics of temperature-sensitive pharmaceuticals… by analyzing data and predicting potential temperature excursions”. In practice, connected sensors monitor cold-chain temperature and humidity throughout transit, automatically alerting operators to any deviation. AI-driven software then adjusts routes on-the-fly (re-routing around traffic or delays) to keep the shipment within required conditions. In short, predictive analytics and continuous monitoring mean fewer spoiled batches and more “on-time in-full” deliveries. This high-tech transparency ensures that vaccines, biologics, and other fragile products remain effective by the time they reach patients
Furthermore, digital platforms (Transport Management Systems) coordinate every step. They enforce compliance by logging chain-of-custody, generating required documentation, and even optimizing last-mile drivers’ schedules. The net result is a logistics network where patients can order a critical medicine online and track it down to a minute, while regulators and providers have full audit trails of each shipment.
Synergy Between OTF Manufacturers and Delivery Networks
Innovations in OTF Manufacturing
As demand for OTFs rises, manufacturers are innovating production methods. One example is ThinOral® Technology (e.g. developed by Zim Laboratories), which enables high-dose thin films with excellent properties. Their patented ThinOral process produces films that are instantly wettable, rapidly dissolving, and non-tacky – even with drug loads up to 50–60 mg per strip. In practical terms, this means potent new medications (larger molecules or higher doses) can finally be formulated as convenient films.
Other manufacturing innovations include layer-by-layer casting, inkjet printing, and roll-to-roll processes. These methods aim to produce films reliably and at scale. For instance, Zim Labs reports a dedicated OTF facility capable of making up to 324 million strips per year. Compared to tablets (which require long compression and coating runs), film manufacturing can be surprisingly efficient – often just mixing ingredients and continuously casting thin sheets, then cutting and packaging. This streamlined process can be run continuously around the clock, vastly accelerating time-to-market for new film-based drugs.
Meeting Demand at Scale
Scaling OTF production, however, comes with challenges. Even with advanced technology, each film can only carry a limited dose, so producing hundreds of thousands of strips to meet demand is no small feat. Quality must be tightly controlled: every square millimeter of film must have uniform thickness and drug content. Manufacturers invest in precision coating machines and rigorous quality control to ensure each film dissolves predictably. These innovations – like high-speed solvent casting and automated inspection – are making OTFs feasible for blockbuster medications, not just niche treatments.
Case Study: Melatonin OTFs + USPS Delivery
Consider a hypothetical example: Circadin is a brand of slow-release melatonin for insomnia. An OTF manufacturer might reformulate 2 mg melatonin into an OTF strip for rapid sleep onset. Once made, these melatonin strips can be distributed directly to patients via mail order. Thanks to USPS’s nationwide network (covering every address in the U.S.) and its proven 1–2 day delivery for test kits, even a small pharmacy can ensure a customer in any state receives the insomnia therapy by the next morning. This synergy – specialized OTF manufacturing plus proven courier logistics – means patients no longer have to wait or travel to clinics for simple prescriptions.
Similarly, chronic-care medications in film form (like daily Parkinson’s or Alzheimer’s drugs) could be automatically refilled and overnighted to patients via rapid mail, ensuring adherence. In each case, the collaboration between an OTF manufacturer and a same-day delivery network creates a new service model: personalized, on-demand medicines made tangible at the point of care.
Challenges and Solutions in OTF and Rapid Logistics
OTF Formulation Challenges
Despite their promise, OTFs pose technical hurdles. A chief challenge is dose uniformity. Because the active drug is dispersed in a thin matrix, the coating process must be precisely controlled. Research warns that “dose uniformity in the film is directly controlled by spray pattern… maintaining such strict control is a challenge” during manufacturing. Small variations in polymer coating or drying can lead to hotspots of API or thin sections. Manufacturers overcome this with tightly regulated solvent casting or hot-melt extrusion processes, and inline monitoring tools (e.g. near-infrared sensors) to verify consistency.
Another issue is limited drug load. Most OTFs can only carry a few milligrams per strip. Highly potent drugs work well, but large-molecule or high-dose therapies remain difficult to fit into a 2″×2″ strip. Enhancing drug solubility and exploiting mucoadhesive layers are areas of ongoing R&D. Additionally, OTFs are inherently moisture-sensitive (hygroscopic), so they require robust barrier packaging and careful storage.
Regulatory Hurdles
Regulatory pathways for OTFs can be complex. Unlike tablets, there are relatively few official pharmacopeial standards for films. For example, the U.S. Pharmacopeia has no dedicated monographs for testing film disintegration or mucoadhesion. This means companies and regulators must negotiate suitable quality tests. Clinical data must also demonstrate bioequivalence (or benefit) to existing products, which can slow approval. Still, agencies are updating guidance: recent OTF drug approvals (e.g. as-needed migraine therapy) show that regulators are increasingly familiar with the technology. Broadly, though, patent expirations and new filings are driving collaboration: contract manufacturers and CDMOs offer tailored OTF development services to navigate these hurdles and bring generics or new uses to market faster.
Delivery Challenges
On the logistics side, last-mile delivery of fragile medications has its own obstacles. Temperature control is paramount: vaccines, biologics, and some small-molecule drugs require refrigerated transit. Modern couriers address this with insulated packaging and IoT temperature loggers. As one expert notes, “[IoT sensors] provide continuous visibility into [shipment] conditions, sending alerts in case of any temperature deviations”. Companies also employ cold-chain certified vehicles and real-time tracking to protect the payload.
Last-mile reliability is another concern. Rural or remote destinations can be hard to reach quickly. To mitigate this, logistics providers establish local hubs or partner with postal networks (e.g. USPS) to cover every address. They also use dynamic route planning: if a traffic jam or outage is detected, AI-powered systems automatically re-route couriers to avoid delays. In effect, the same technology that tracks a pizza delivery in real time is now applied to ensure a vial of insulin stays within spec on its journey.
Security protocols are equally important. High-value or controlled medications must be guarded against theft or tampering. Providers like Dynamex enforce strict chain-of-custody measures: drivers undergo background checks, vehicles are GPS-monitored, and packages often have tamper-evident seals. Every step is logged digitally, which both meets regulatory requirements (Good Distribution Practices) and reassures manufacturers. Robust tracking and driver training minimize the risk that a critical shipment could be compromised in transit.
Despite these challenges, the industry’s solutions are rapidly evolving. Transport Management Systems integrate all these safeguards – temperature alerts, GPS tracking, compliance documentation – into a unified view. This ensures that, even for the most sensitive OTF drug, a patient can be confident that “what was prescribed is what’s inside the bottle (or film packet)” upon arrival.
Future Trends: Faster, Smarter, and More Accessible
Looking ahead, the pace of innovation in both film technology and logistics shows no sign of slowing. On the formulation front, researchers are developing “smart” films that do more than dissolve. For example, some experimental OTFs incorporate sensor patches or inkjet-printed electronics that could monitor patient use or trigger drug release in response to a physiological signal. Biodegradability is another trend: new film polymers that break down harmlessly after ingestion are in development, reducing packaging waste.
In logistics, drone delivery and autonomous vehicles are becoming feasible for healthcare. Amazon’s trial of drone prescription delivery (under 1-hour service in Texas) hints at a future where remote clinics or homes get urgent meds by air. Besides speed, blockchain technology is poised to bolster the supply chain. By encoding each drug’s origin, formulation, and handling into an immutable ledger, blockchain could prevent counterfeiting and improve recall tracking. Several pilot projects are already using distributed ledgers to trace vaccine lots and high-value biologics from factory to patient.
Finally, AI and analytics will continue to refine efficiency. Advanced algorithms will predict demand hotspots (e.g. a flu outbreak) and pre-position inventory at local mail hubs. Network-wide data analysis can flag potential disruptions (weather, supplier shortages) before they occur, enabling proactive rerouting or rescheduling. The end result will be a healthcare supply chain that is not just fast, but truly intelligent: it learns from every shipment to become safer and more reliable.
Conclusion: A New Era of Healthcare Efficiency
The convergence of oral thin film drug delivery and lightning-fast logistics is ushering in a new era of healthcare efficiency. For pharmaceutical manufacturers and outsourcing partners, this means a compelling opportunity: by adopting OTF technology and partnering with advanced couriers, they can deliver innovative therapies with unprecedented convenience. Whether you’re a CDMO looking to expand your services, or a supplier seeking to offer a novel dosage form, the time to invest in OTF capabilities is now.
Ultimately, the future of medicine will be defined as much by how drugs are delivered as by the drugs themselves. Film-based medicines, carried by same-day or next-day networks, exemplify the very best of drug delivery innovation. They promise not only improved patient compliance and outcomes, but also leaner supply chains and new markets. By embracing these trends – from thin-film manufacturing breakthroughs to AI-driven postal delivery – healthcare suppliers and manufacturers can stay ahead of the curve and meet the next wave of patient needs. The patient of tomorrow will receive personalized, sophisticated treatments faster and more seamlessly than ever before, and companies that enable this will be the leaders in 21st-century pharmaceutical supply.
